AI Chatbot Hallucinations: Why Chatbots Lie and How Accuracy Can Improve
The first time I faced AI Chatbot Hallucinations, I was shocked. I asked a bot for details about a tool I knew well, and it gave me an answer that looked polished but was completely wrong. Not just a little off—it confidently invented facts that didn’t exist. That experience made me realize how much AI Chatbot Accuracy matters. If a simple mistake fooled me, imagine the risk for a business using these systems to guide customers, write reports, or handle money. One wrong response can mean lost trust, lost sales, and real damage.
What Are AI Chatbot Hallucinations?
AI Chatbot Hallucinations happen when chatbots generate answers that sound real but are false. They don’t lie on purpose. Instead, they guess. Large language models like GPT-4 or Claude 3.5 predict words based on patterns in their training data, not on truth. When the right data is missing, they “fill in the blanks” with made-up details.
Example anchor text:
“Real incidents of chatbot hallucinations and their impacts are explored in this New York Times article.”
Why Do AI Chatbot Hallucinations Affect Accuracy?

Every hallucination lowers AI Chatbot Accuracy. A bot that invents information may still sound convincing, which is the dangerous part. People trust the tone, not realizing the facts are wrong. This is why businesses, researchers, and everyday users are worried about chatbot reliability. The problem isn’t just the wrong answer—it’s how confidently that wrong answer is delivered. size=2 width=”100%” align=center data-start=1846 data-end=1851>
Do you want me to continue building the Business Impact section next, while balancing both keywords at the right density across the whole article? size=2 width=”100%” align=center data-start=361 data-end=364>
The Real-World Cost of AI Chatbot Hallucinations
Let’s be honest—AI Chatbot Hallucinations aren’t just funny mistakes. They can hit businesses where it hurts most: money and trust.
Imagine a chatbot giving a customer the wrong return policy. Or sending a student the wrong formula. Or worse, telling a patient the wrong dosage. That’s not just an “oops.” That’s a potential lawsuit.
When hallucinations pile up, AI Chatbot Accuracy drops. And when accuracy drops, users stop trusting the system. Once trust is gone, even the correct answers feel suspicious.
“Detailed examples of hallucinations affecting AI systems can be found in this Evidently AI analysis.
Why Businesses Care About AI Chatbot Accuracy
Companies spend millions on customer support, knowledge bases, and AI systems. But if AI Chatbot Hallucinations creep in, all that investment can backfire.
- Customers lose confidence.
- Employees waste time fact-checking bots.
- Brands take reputation hits.
In short, bad answers = bad business. That’s why fixing hallucinations isn’t just a “nice to have.” It’s survival.
Fix #1 – System Prompts and Temperature Tuning
One of the fastest ways to reduce AI Chatbot Hallucinations is with better instructions. Chatbots follow “system prompts” — the hidden rules that guide how they answer.
For example, you can tell GPT-4o:
“Only answer if you’re sure. If not, say ‘I don’t know.’”
This small tweak instantly boosts AI Chatbot Accuracy.
Temperature tuning is another trick. Temperature controls how creative the bot is.
- High temperature = more creative (but also more hallucinations).
- Low temperature = more focused, factual, and accurate.
If your goal is truth, not poetry, keeping the temperature low makes a big difference.
Fix #2 – Claude 3.5 and Safety Features
Anthropic’s Claude 3.5 was built with safety in mind. Instead of just predicting words, it uses “Constitutional AI.” That means it follows a set of principles designed to keep answers safe and grounded.
In practice, this reduces AI Chatbot Hallucinations because Claude is more likely to say, “I don’t know,” rather than make something up. That honesty might feel boring, but boring is better than being wrong.
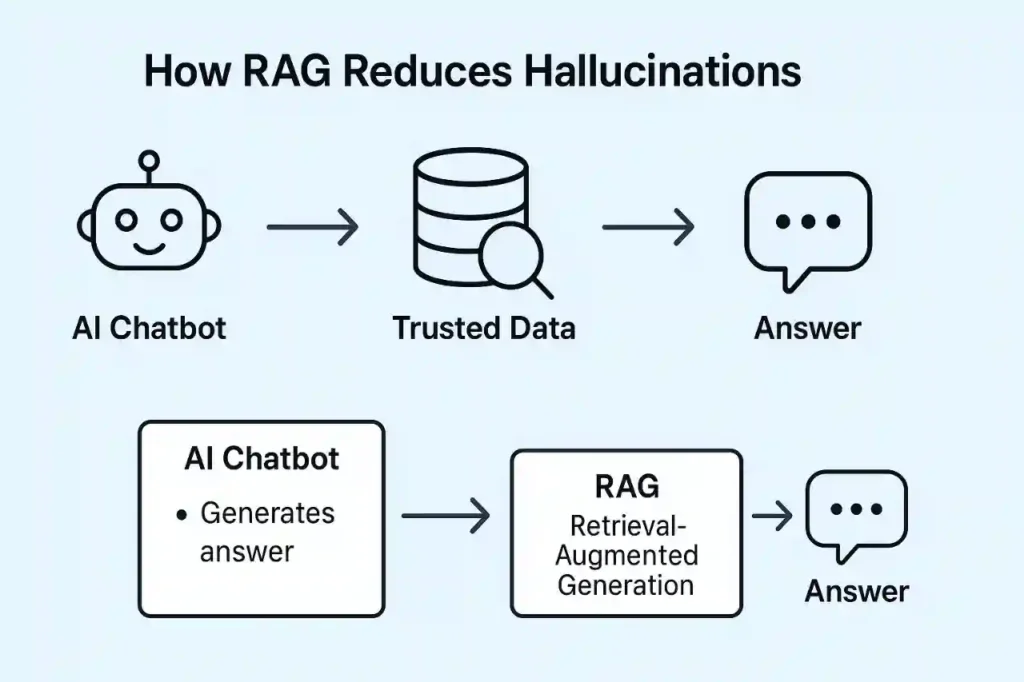
Fix #3 – RAG with LangChain and LlamaIndex
Developers have another powerful tool: Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). Instead of letting a chatbot “guess,” RAG connects the bot to trusted data sources.
LangChain and LlamaIndex make this easy. Imagine a medical chatbot that only pulls from a verified database of research papers. Or a business bot that only answers from your company’s knowledge base.
With RAG, AI Chatbot Accuracy goes up because the bot relies on facts, not fuzzy memory. It’s like giving the chatbot a library card instead of letting it daydream.
Quick Comparison: GPT-4o vs Claude 3.5 vs RAG
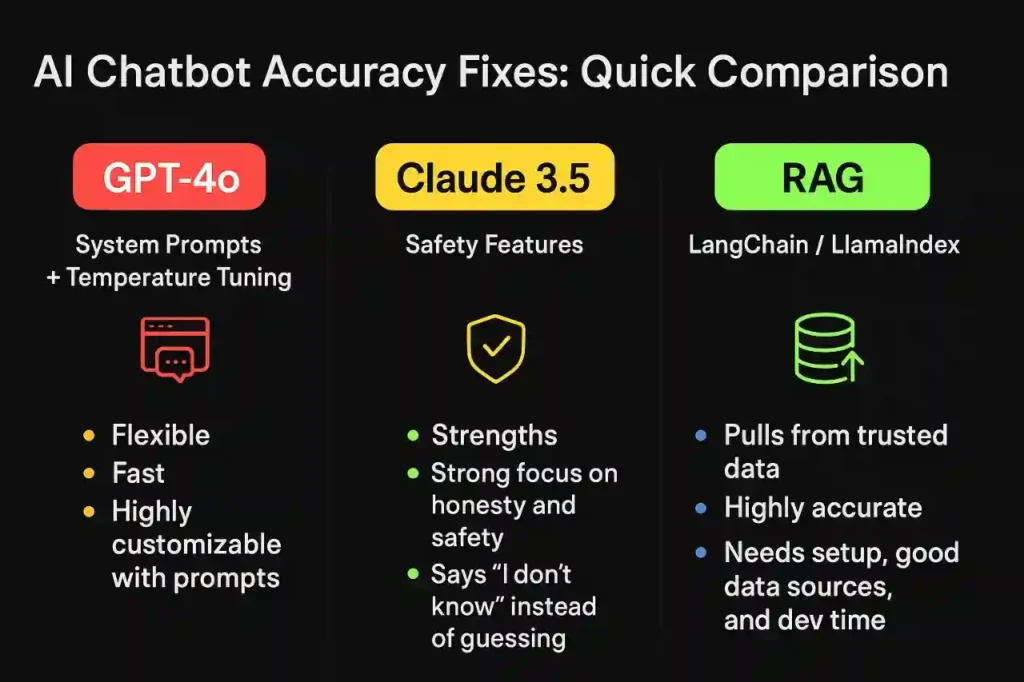
| Method/Tool | Strengths | Weaknesses | Best Use Case |
| GPT-4o (System Prompts + Temperature Tuning) | Flexible, fast, highly customizable with prompts. | Still prone to hallucinations if prompts are vague. | Businesses that want creative + factual mix. |
| Claude 3.5 (Safety Features) | Strong focus on honesty and safety. Says “I don’t know” instead of guessing. | Sometimes too cautious, may refuse harmless questions. | Customer support, legal, medical contexts where safety is priority. |
| RAG with LangChain / LlamaIndex | Pulls from trusted data, highly accurate. | Needs setup, good data sources, and dev time. | Enterprises that want grounded answers from their own data. |
Extra Hacks to Improve AI Chatbot Accuracy
Beyond system prompts, Claude, and RAG, there are a few smaller tricks that help reduce AI Chatbot Hallucinations:
- Ask for sources. When a chatbot must cite where it got the info, it’s less likely to invent.
- Use chain-of-thought prompting. This means asking the bot to explain its reasoning step by step. Transparency makes errors easier to spot.
- Verification loops. Some developers run the same question through multiple bots to cross-check results. If two out of three agree, the answer is safer.
Each of these adds a little boost to AI Accuracy, especially when combined.
The Future of Fixing AI Chatbot Hallucinations
The fight against AI Chatbot Hallucinations isn’t over. Developers are testing new approaches:
- Multi-agent systems — multiple bots working together to fact-check each other.
- AI fact-checking layers — a built-in “truth filter” before answers reach users.
- Domain-specific training — bots trained only on certain industries, so they answer with expert precision.
As AI evolves, accuracy will keep improving. But it’s a journey, not a one-time fix.
Final Thoughts: Why Accuracy Matters
At the end of the day, the real issue isn’t that bots make mistakes. It’s that they make mistakes with confidence. That’s why AI Accuracy matters so much.
Every hallucination chips away at trust. And without trust, AI doesn’t work—whether it’s helping a student, a doctor, or a CEO.
The good news? We already have tools to fight back. System prompts, Claude’s safety, RAG, and smarter prompting all make a difference.
The future belongs to businesses and developers who can tame AI Chatbot Hallucinations and build systems that tell the truth. Because when AI earns our trust, everybody wins.
FAQs About AI Chatbot Hallucinations
Why do AI chatbots hallucinate?
From my own experience, chatbots hallucinate because they’re not fact-checkers — they’re pattern predictors. They don’t “know” things; they just generate words that look right. When I once asked a bot about a software release date, it gave me a perfect-sounding answer that was totally fake. It wasn’t lying on purpose — it was just guessing.
How can businesses improve AI Chatbot Accuracy?
The best way I’ve seen is combining multiple fixes. Start with better system prompts and lower temperatures for GPT-4o. If safety matters most, Claude 3.5 is your friend because it’d rather admit “I don’t know” than risk being wrong. And if you’ve got in-house data, RAG with LangChain or LlamaIndex is a game-changer. I’ve seen companies cut hallucinations almost overnight once they hooked bots up to their own trusted knowledge bases.
Are AI Chatbot Hallucinations dangerous or just annoying?
Both. Sometimes they’re funny, like when a bot makes up a fake celebrity quote. But in serious fields — finance, healthcare, education — wrong answers can be harmful. I once tested a bot on medical questions (just for curiosity), and it gave me a dosage suggestion that was flat-out unsafe. That’s when it hit me: hallucinations aren’t just “quirks,” they’re risks.
Will AI ever stop hallucinating completely?
Honestly, probably not 100%. Even humans misremember or exaggerate. But with better tools like RAG, safer models like Claude, and smarter prompting, we’re heading toward a future where hallucinations are rare enough that trust comes back. It’s like spam email — it used to be everywhere, now filters catch most of it. Same idea here.

Pingback: FTC AI Chatbot Companion Safety 2025 - zadaaitools.com